
Tissue Transplants: Graft and Flap Techniques
In cases such as injuries, tumor surgery, inflammatory processes, or severe infections that result in tissue defects that cannot be closed directly, tissue repair is usually performed using tissues taken from the patient’s own body. In the treatment of such tissue losses, the correct choice of technique and method directly affects the success of healing.
If the transplanted tissue survives passively with the recipient site’s blood supply and does not require an external vascular connection, it is called a graft. Grafts are usually taken from skin, cartilage, or bone tissue and are used to repair tissue deficiencies in certain parts of the body.
On the other hand, if the transplanted tissue is transferred with its own vascular structure preserved, either without interrupting the blood supply or by reconnecting the vessels using microsurgical techniques, this procedure is called flap surgery. The flap method is often preferred for the treatment of larger and more complex tissue defects.
The choice between graft or flap depends on the size of the defect, the patient’s general condition, and the surgeon’s experience. With the right method, tissue repair provides both functional and aesthetic success.
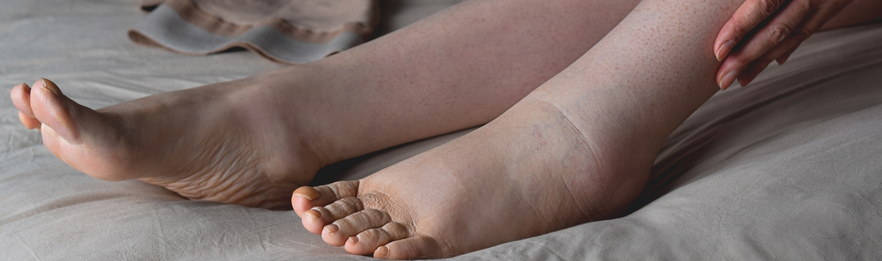
Lymphedema: Swelling Caused by Lymphatic Obstruction and Treatment Methods
Blockages in the lymph nodes, which are part of the immune system, prevent lymph fluid from draining, leading to swelling in certain areas of the body. This condition, medically called lymphedema, is not only aesthetically disturbing but can also cause functional problems. Common issues include difficulty wearing clothes, shoes, watches, or rings.
The most common symptom of lymphedema is swelling, accompanied by pain, a feeling of pressure, thickening, and hardening of the skin. In advanced cases, leakage of fluid from the skin may occur, further reducing quality of life and increasing the severity of the disease.
The most common cause of lymphedema is the removal of lymph nodes during cancer treatment. Radiation therapy, fungal infections, trauma, infections, and surgical procedures that damage lymphatic pathways can also play a role in its development.
In many cases, lymphedema can be easily diagnosed through physical examination. It is also known among the public as “elephantiasis.” Treatment methods include manual lymph drainage, compression therapy, exercise programs, and skin care. In suitable patients, advanced techniques such as lymph node transfer, microsurgical connections, and liposuction may also be applied. When diagnosed early, the negative effects of lymphedema can largely be controlled. However, as the disease progresses, especially with severe swelling in the arms or legs, treatment becomes more difficult. Therefore, expert medical follow-up and regular intervention are of great importance.
About the Author
Prof. Dr. Osman Kelahmetoğlu
Specialist in Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery
This article was prepared by Prof. Dr. Osman Kelahmetoğlu based on scientific sources and clinical experience. You may contact us for more information or to schedule an appointment.
Contact: iletisim@osmankelahmetoglu.com – 0 (533) 351 76 37
